Korea CSP

Provide Feedback
CloseShare With Contacts
CloseShare With Contacts
CloseCopy Link
Closehttps://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Delete Message?
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
An update is now available for this app!

You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
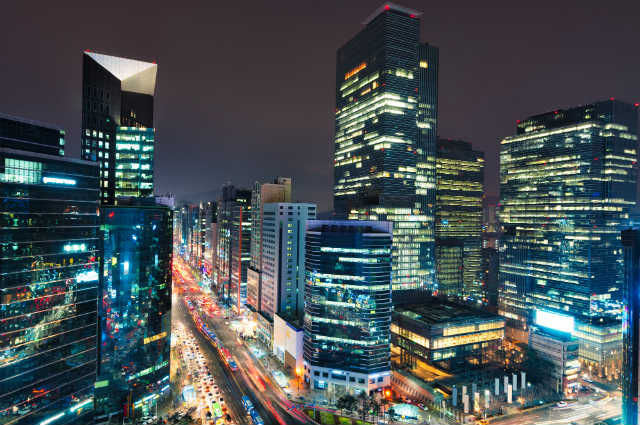
The Republic of Korea (ROK), commonly known as Korea, is the fourth-largest economy in Asia and the 13th largest in the world. It is an innovative, free-market economy with a highly educated workforce and democratic government.
Korea is an optimal location for doing business with the world's second and third-largest economies (China and Japan) and engaging the overall Asian market. Korea is located within an average travel time of three hours from more than 81 cities with a population of one million or more. Coupled with its world-class infrastructure, Korea is an ideal location for Australian businesses looking for a Northsian hub.
Korea is Australia's fourth largest trading partner, with two-way trade totalling over AUD 33.8 billion in 2015-16. Australia and Korea enjoy a complementary trade relationship – Australia sending raw materials to Korea and Korea exporting manufactured goods to Australia. Services are also an increasingly important aspect of the trade relationship, and investment is growing from a relatively low base. Korea has an advanced manufacturing sector and is home to iconic and world leading brands such as Samsung, LG, Hyundai and Kia. The nation boasts an affluent, tech savvy population with a well-educated, highly skilled workforce.
The Korea Australia Free Trade Agreement (KAFTA), which came into force in December 2014, has opened up even more opportunities for Australian business. There are several industries that Australian businesses can target and take advantage of.

Food and agriculture: Korea is highly dependent on food imports, with agricultural imports totalling AUD 35 billion per year. Australian businesses are well regarded in Korea as suppliers of high quality and safe food. Opportunities exist for Australian businesses in a range of food and agricultural items such as wine, nuts, dairy, meat and fresh fruits.
Financial services: Korea's rapidly ageing population needs increased financial security from personal investments. Consumer expectations are driving greater interest by institutions in higher yield “alternative" products, such as offshore investment services, and partnerships with foreign firms. Infrastructure and real estate are two areas of particular interest for many Korean firms.
Education: Korea is a stable and well-established market for Australian education providers. It is the fourth-largest source country for foreign students in Australia after China, India, and Vietnam. Opportunities for Australian institutions exist in higher education, vocational education and training (VET), schooling, and intensive English courses.
Professional services: The free trade agreement will deliver new opportunities for Australian service suppliers, particularly in accounting, legal and audiovisual services.
ICT digital content and services: Koreans are among the world's biggest users of fast broadband and mobile phones. Korea was the first country to build a national, high-speed fibre broadband network, and has a mobile penetration rate of 1.1 mobile phones per person.
Health, aged care and biotech: Korea's population is ageing rapidly, generating increased demand for aged care, the biotech industry, medical services and devices, over-the-counter medications and rehabilitation services.
Innovative with a strong commitment to R&D: Korean investment in research and development was USD 80 billion (AUD 108 billion), or 4.3 per cent of GDP in 2016 – one of the highest levels in the world. Koreans love new technology, and are often among the first in the world to embrace cutting edge products and services. This, along with Korea's superb infrastructure, makes it an ideal test bed for innovative foreign manufacturers and service providers.
Safe, stable and developed: Korea is one of 34 OECD member states. Sovereign risk is low, with a high investment grade rating on its government debt (Ranking - S&P: AA+,Fitch: AA- and Moody's: Aa2).

For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
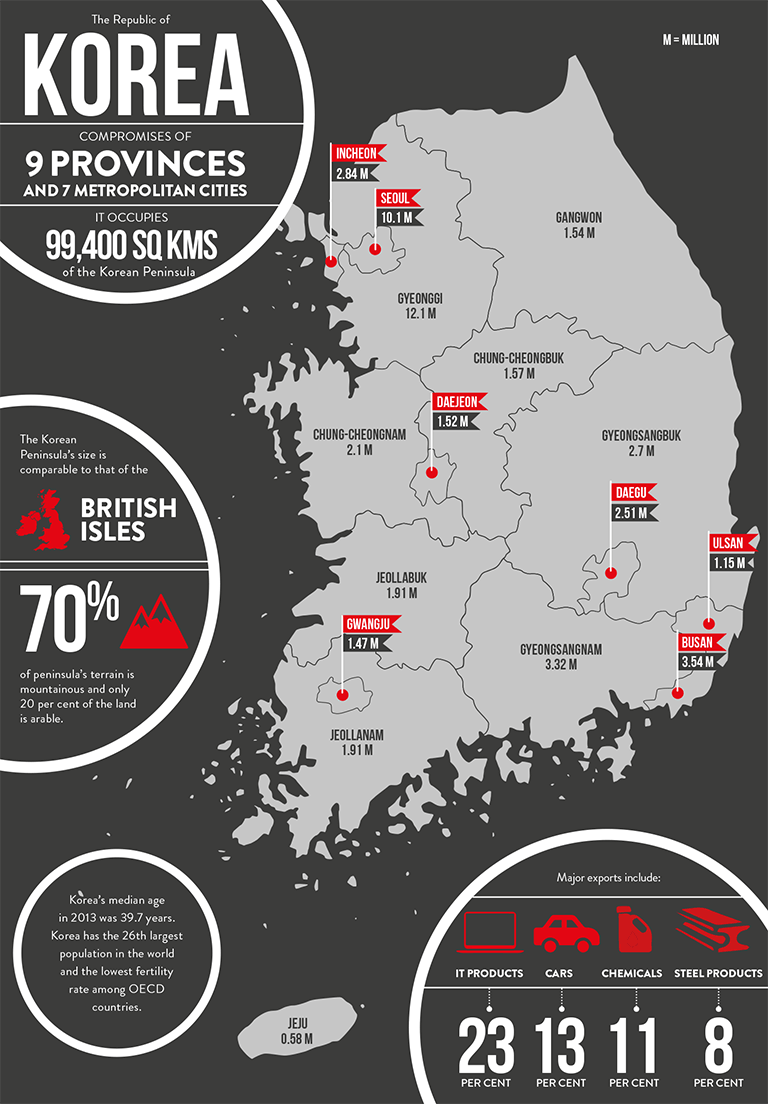
Korea occupies 99,400 square kilometres of the Korean Peninsula in North Asia, between Japan and China. North Korea is slightly larger, at 122,400 square kilometres. Korea and North Korea are separated by a demilitarised zone established after the Korean War of the 1950s. With a mostly mountainous terrain (70 per cent), only 20 per cent of the land in Korea is arable
Korea comprises nine provinces with seven metropolitan cities: Seoul, Busan, Gwangju, Daejeon, Daegu, Ulsan and Incheon.
The Korean climate has four distinct seasons. Temperatures reach up 38°C in summer, while winter temperatures average -7° to 1°C with moderate snowfall. Average annual rainfall ranges from 115 to 125 centimetres, of which almost half occurs during the monsoon season in July and August.
An independent Korean state or group of Korean states has existed almost continuously for several millennia. Like Japan, Vietnam, and a number of other states in East Asia, successive Korean dynasties acknowledged China as the centre of civilisation and paid symbolic tribute to the Chinese emperor. In practice, Korea was independent of China and developed its own distinct culture and political systems.
In 1910 Japan annexed Korea as a colony, ending the Joseon dynasty after more than 500 years of independent rule. Following Japan's defeat in World War II, Korea was temporarily divided, with the United States administering the southern half of the Peninsula and the Soviet Union the area north of the 38th parallel. In 1948, new governments were established in each zone – the Republic of Korea in the south and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea in the north. Unresolved tensions between the two led to the Korean War of 1950-53. An armistice ended the fighting but a more comprehensive peace agreement has not been negotiated. Relations between North Korea and Korea remain tense.
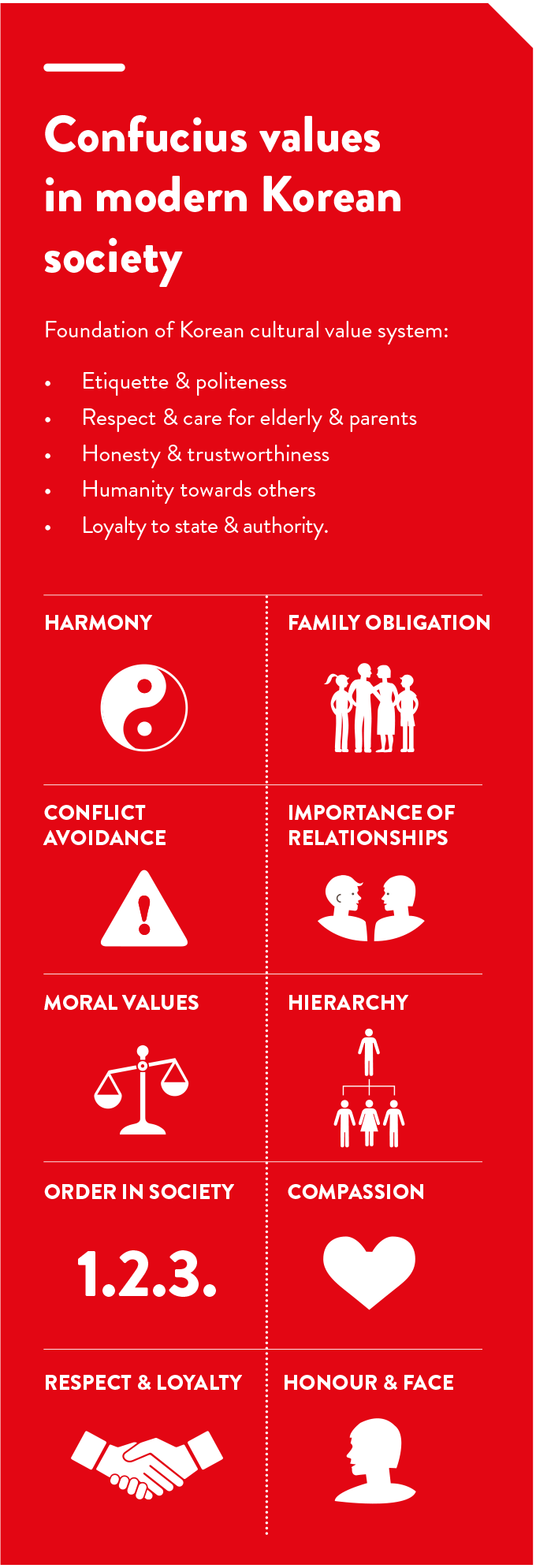
Koreans are proud of their cultural heritage. While sharing similarities with the Chinese and Japanese, Koreans have maintained their distinctive language, culture and customs. The highly authoritarian, male-dominated system of Confucianism is reflected in the paternalistic and male-dominated Korean culture. Overall, it is a conservative society with importance placed on education, social status and role, relationships, gender and respect.
Maintaining face is central to business and social relationships. Koreans aim to preserve a harmonious environment in which a person's kibun (mood or inner feelings) can remain balanced. The best way to handle kibun is not to demand yes or no answers and to accept the need for slow consensual decision-making. Contradicting someone or criticising them in front of others are sure ways to lose business.
Religion plays an increasingly significant role in the lives of Koreans. More than 53 per cent of Koreans now follow a specific religious faith. Buddhists account for some 43 per cent of the religious population, followed by Protestants at more than 34 per cent and Catholics at more than 20 per cent.
Koreans possess a remarkably ambitious mindset. They have a word – han – to describe the urge to overcome obstacles and reach out for victory. Han is everywhere: in working culture, education and everyday life. It is no surprise that Koreans work more hours per capita than the citizens of any other OECD nation.
Koreans are among the world's most educated people, according to OECD statistics. A large percentage of family income is typically spent on providing the best possible education for the children. The culturally ambitious mindset of Koreans and their focus on education have been vital factors in the country's outstanding economic success.
Korea has a presidential system of government. Power is shared by three branches: the executive (headed by the President), the legislature (a single-house National Assembly), and the judiciary. Legislative power is vested in the unicameral National Assembly, comprising 300 members elected for four-year terms.
The President, limited to serving a single five year term holds supreme power over all executive functions of government, within the constraints of the Constitution. The President appoints public officials, including the Prime Minister (with the approval of the National Assembly), ministers (who do not need to be members of the National Assembly), and the heads of other executive agencies. The President is also commander-inchief of the armed forces. Moon Jae-in is the current President of the Republic of Korea. He won the May 2017 Presidential Election and was inaugurated on 10 May 2017. President Moon will serve until the end of his five year term in 2022.
Korea is the world's 13th-largest economy with a GDP of US$1.435 trillion in 2015. Advanced manufacturing and services dominate the economy. Among its main manufactures are mobile phones, consumer electronics, whitegoods, cars, ships and steel, exported around the globe. Korea imports large quantities of natural resources such as coal, iron ore and oil, and is a net importer of agricultural products.
Korea's phenomenal economic progress in the last half-century has in many ways mirrored the Japanese “economic miracle" that preceded it. In the 1970s and 1980s, the Government channelled capital into family-controlled chaebols (conglomerates) enjoying trade preferences and monopoly rights. This enabled the chaebols, which today include the Hyundai and Samsung groups, to grow into massive business empires.
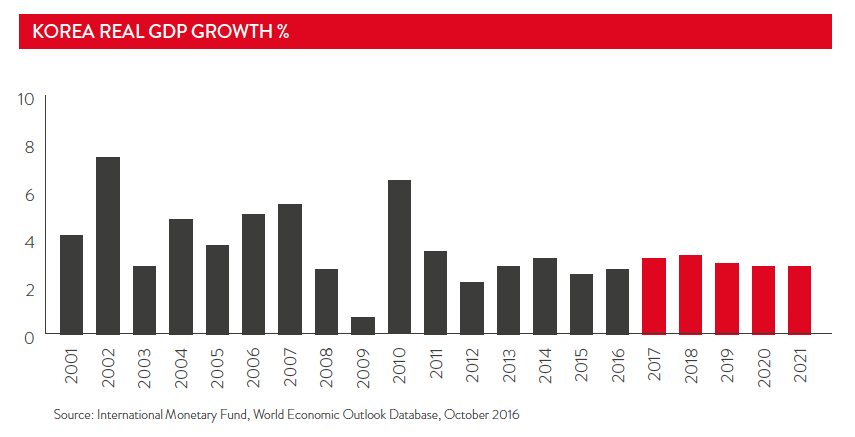
By 2014, Korea had risen to be the world's sixth-largest exporter and seventh-largest importer. With high-tech industry and a sophisticated consumer market, Korea offers an attractive market for businesses to begin or expand their Asian presence. It is the world's largest shipbuilder, fifth-largest car maker, and sixth-largest steel maker. Foreign investors can obtain returns by utilising the skilled workforce in high-value and high-technology fields.
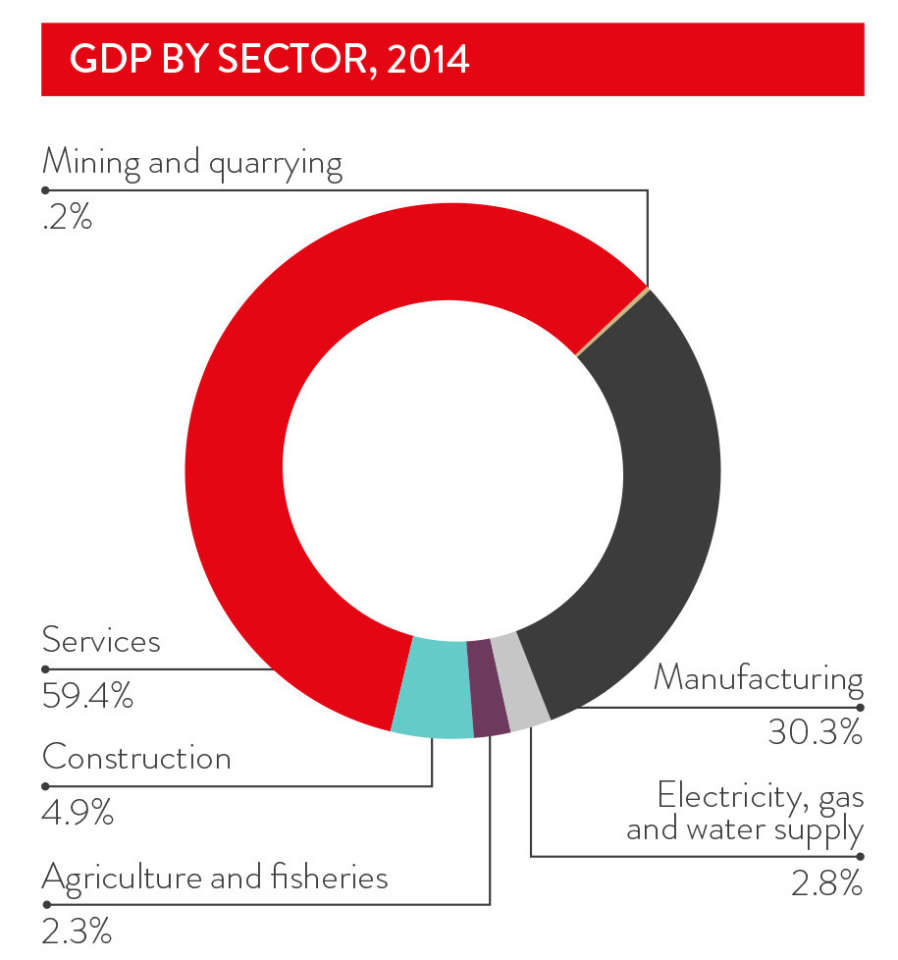
Manufacturing has transformed Korea into a global industrial giant. It is one of the world's largest shipbuilders, fifth-largest car maker, and sixth-largest steel maker. In the past, most opportunities for foreigners have involved establishing labour-intensive manufacturing or processing operations. These days, investors obtain better returns by utilising the skilled workforce in higher-value and high-technology fields.
Korea's services sector has long lagged behind its manufacturing sector in efficiency and effectiveness. As part of a three-year growth plan unveiled in 2014, the Government identified healthcare, education, finance, tourism and software as key services sector industries.
Korea has a three-tiered, independent judicial system, comprising the Supreme Court, the Constitutional Court, six High Courts, 13 District Courts and several courts of specialised jurisdiction, such as the Family Court and Administrative Court. There is no jury system in Korea, although since 2008 a limited system has been adopted for criminal and environmental cases. But all questions of law and fact are decided by judges.
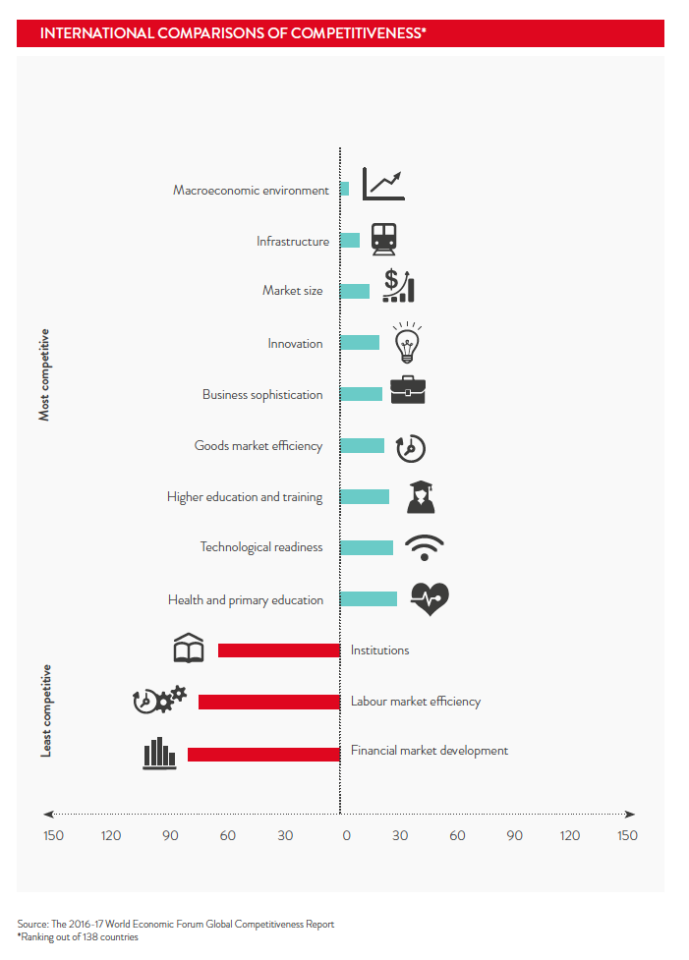
One of the biggest advantages of doing business with Korea is its advanced transport infrastructure. The World Economic Forum Global Competitiveness Report 2016-17 ranked Korea's infrastructure at 10th in the world.

All major Korean cities are connected by expressways and the super high-speed rail system, Korea Train eXpress (KTX). Seoul has a dependable mass transit system of subways, and taxis are plentiful. Korea also has world-class logistics hubs. Incheon International Airport is the world's fifth largest in terms of international air cargo volume, handling 2.6 million tons in 2015.
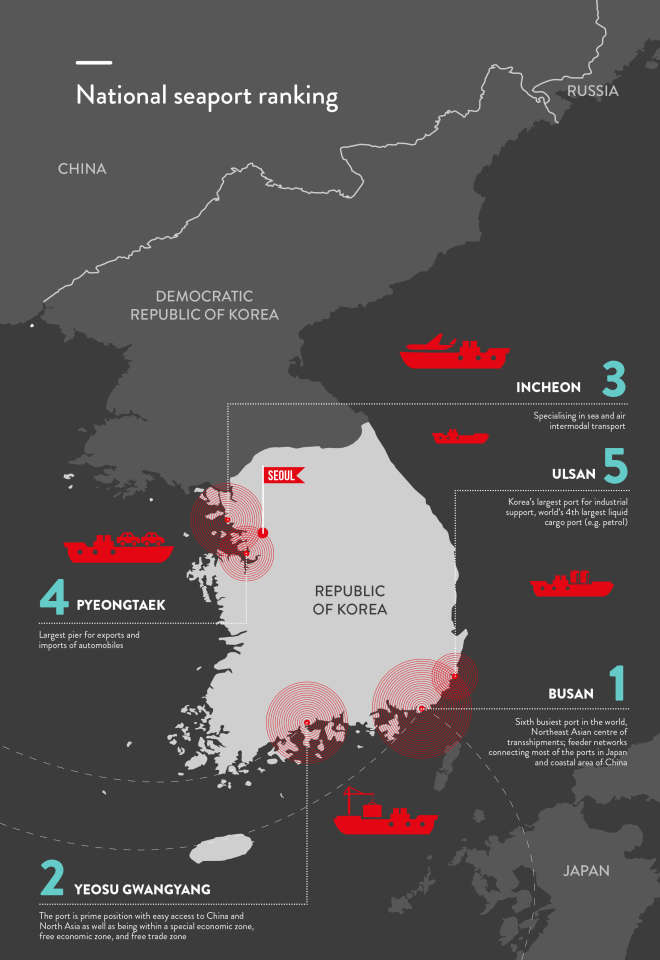
Container ships from Korea ply international sea lanes to ports in America, Europe, Australia, the Middle East and Africa. Port cargo volume has climbed steadily, with the expansion of port facilities and increased productivity through improved cargo-handling capabilities at Busan, Gwangyang and Incheon.
Korea is a leader in information and communications technology (ICT). This is demonstrated by its vast ICT-related production and exports, world-class technology, and the wide use of internet and mobile communication devices in the country. ICT industry-related products, such as computer chips and mobile phones, account for over 23 per cent of Korea's total exports.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
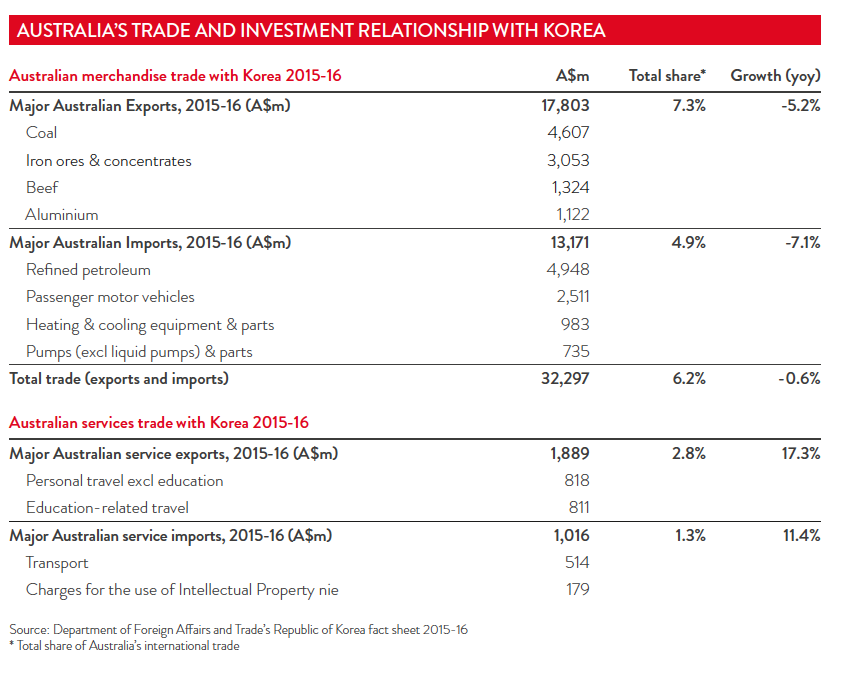
Australia's booming trade relationship with Korea has its origins in the 1960s, when Korea's post-war industrialisation started to fuel its demand for raw materials. Australia became a major supplier to the next Asian miracle, and today names like Hyundai, Kia, Samsung and LG have a place in the hearts of Australian consumers.
Annual two-way trade between Australia and Korea is just under AUD 34 billion, which makes Korea our fourth biggest global trading partner, behind only China, Japan and the United States, and our third largest export market in front of the United States. Total trade (including services) between the two nations is worth around AUD 33.9 billion. Australian merchandise exports to Korea were valued at AUD 17.8 billion in 2015-16 and service exports totaled AUD 1.6 billion.
Australian exports of services to Korea mostly consist of education-related travel and recreational travel. Education has been a major source of growth.
The Korea Australia Free Trade Agreement (KAFTA) came into force on 12 December 2014, delivering big improvements in market access and tariff elimination or reduction. It also substantially improves investment protections for Australians doing business with Korea. The agreement secures Australia's competitive position in the Korean market, where some competitors have been enjoying preferential access. Benefits for Australian businesses through KAFTA include:
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?

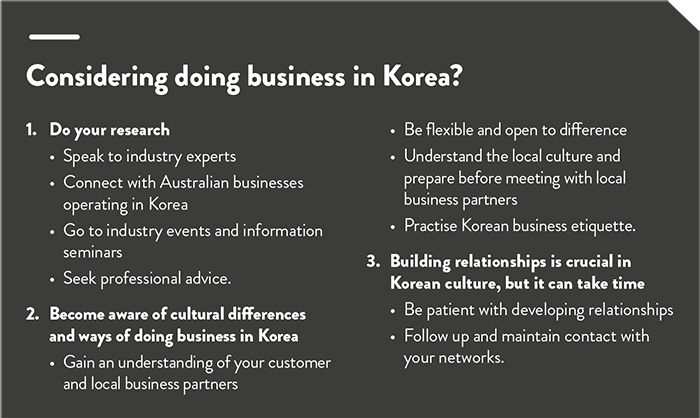
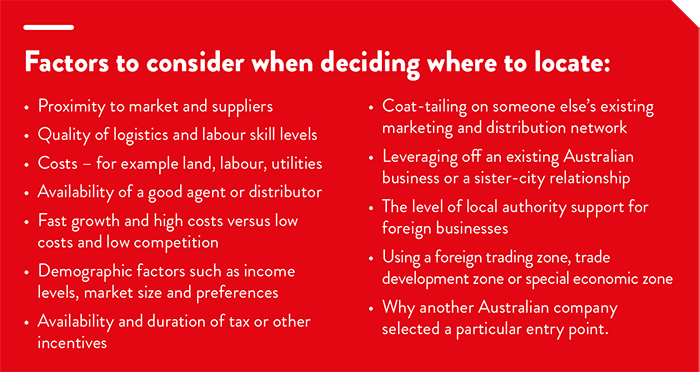
Thorough research is vital as you plan your first moves. You will need to become informed on a wide range of subjects, from industrial relations and tax provisions to labour regulations. Key considerations include choosing a location, assessing the potential risks of operating in a foreign environment, and potential business structures.
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You should develop a Korea strategy before deciding on how to launch you business there. In particular:

Companies looking to enter the Korean market have many location options. While Korea is geographically compact, regional differences need to be taken into account. The country is well served by world-class infrastructure and transportation.
Northwest (Gyeongi, Chungcheongbuk and Chungcheongnam): This includes the economic and political centre of Seoul, with half of Korea's population living in the Seoul Capital Area. Heavy industry and transportation links are located around the port city of Incheon. Daejeon to the south is a major transport hub and centre for research and development.
Northeast (Gangwon): A sparsely populated, mountainous region predominantly focused on agriculture and domestic tourism.
Southeast (Gyeongseongbuk and Gyeongseongnam): Location of Korea's second-largest city, Busan, a major international port. This region is home to heavy industries such as shipbuilding, steel making and automotive production.
Southwest (Jeollabuk, Jeollanam and Jeju): Less developed than neighbouring provinces, agriculture is a significant part of the local economy, though green technology and tourism are increasingly important.
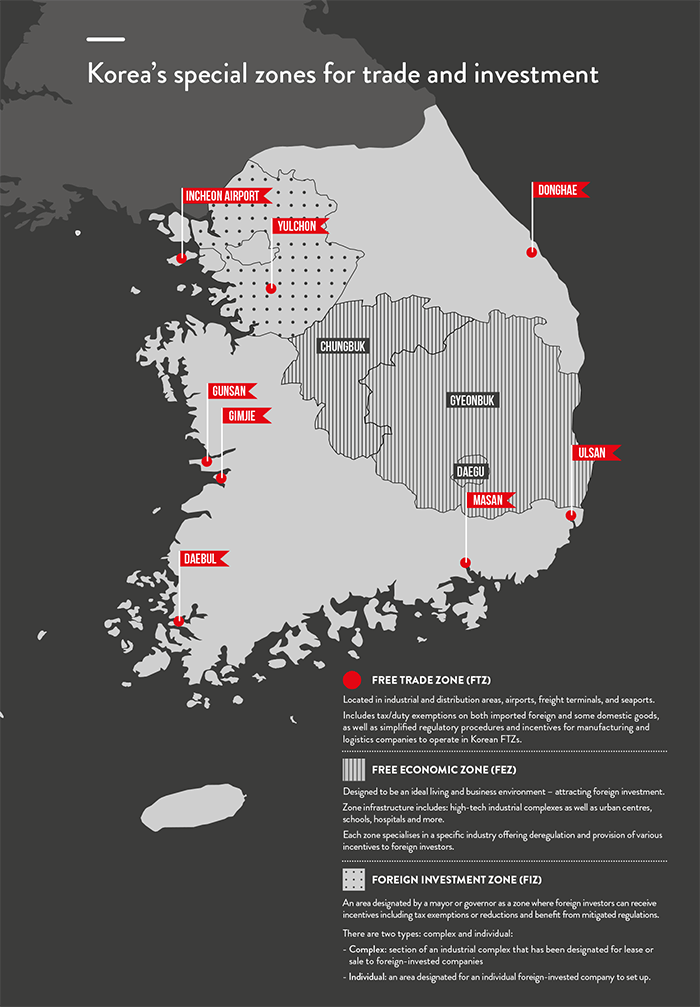
Free trade, foreign investment and free economic zones: The Korean Government has established a number of free trade, foreign investment and free economic zones that provide incentives and tax benefits for foreign businesses.
Korea's official national language is Korean. However, most Koreans engaged in international business speak English. In most business situations an interpreter is not necessary, but it can be an advantage in complex negotiations and when dealing with large groups.
Interpreters are not necessarily translators; the two skills are very different and not always interchangeable. Interpreters are used for interpreting speech; translators for deciphering the written word. Decide which one you want.
Getting to grips with the likely costs of running your business is critical. Key differences operating in Korea can include:
Adequate funding will be critical to your success. You may be eligible for financing from a variety of sources in Australia, including grants, venture capital and equity-sharing deals. However, banks remain the easiest and most approachable source of funding. You could consider a joint-venture arrangement with a trusted partner in Korea, or equity investment from an “angel investor".
Going offshore entails increased risks that need to be identified, managed, and reduced as far as possible. Your business's risk management strategy must also include thorough due diligence.
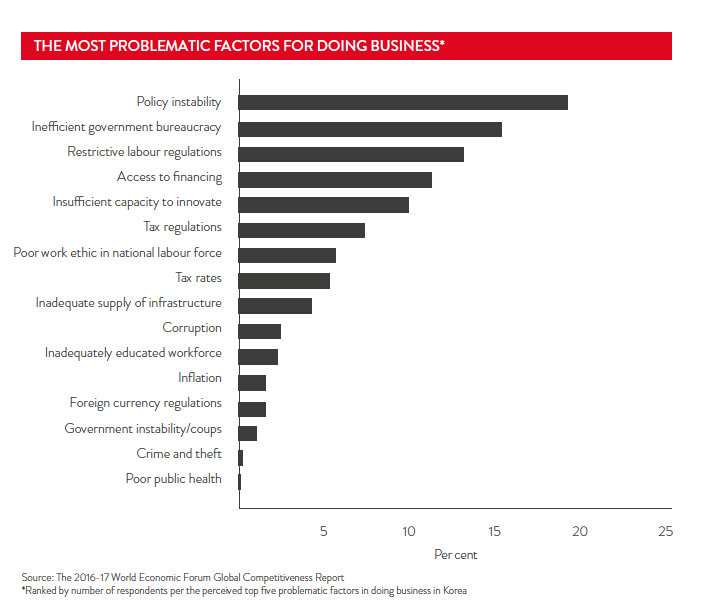
Korea is considered a relatively low-risk destination for doing business in Asia. Korea's sovereign risk is low, with an AA credit rating from Standard & Poor's. The country also ranks fourth out of 189 in the World Bank's Doing Business Report 2017. In 2016, Korea was ranked 52 nd out of 176 countries on Transparency International's Corruption Perception Index.
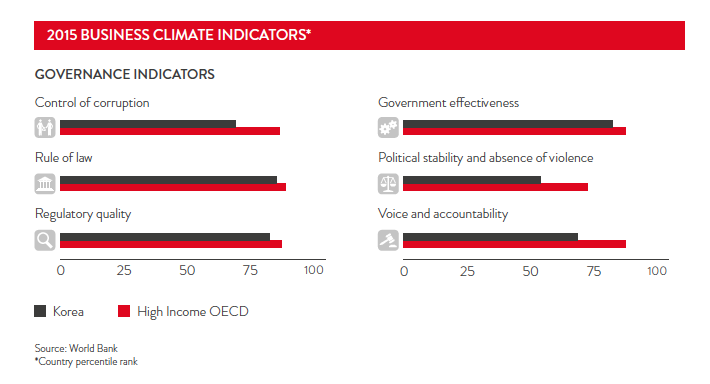
The World Bank's Governance Indicators demonstrate Korea is overall in the top 50 per cent in all areas of governance. Political stability and absence of violence scores are particularly low but the instability with neighbouring North Korea does pose a security threat. According to Australia's export credit agency the Export Finance Insurance Corporation (efic), Australian businesses establishing in Korea should be aware of the considerable market power of the long-standing chaebols (conglomerates of family-controlled firms).
Regional political risk: Tensions remain high on the Korean Peninsula, and the potential for armed conflict between the Republic of Korea and the nuclear-armed communist Democratic People's Republic of Korea remains. Historical grievances against Japan and an ongoing territorial dispute with Japan over an island known as Dokdo by the Koreans are also a source of ongoing political tension.
Protests: Korea is a stable and democratic society. However, disruptive and at times violent protests do occur. The most likely effect of protests would be inconvenience in getting to eetings. Korea has been a member state of the International Labour Organisation (ILO) since 1991. Trade unions are legal in Korea but only 11 per cent of the workforce belongs to one. The suppression of illegal strikes has been known to result in heated confrontation between demonstrators and the police.

For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Comprehensive research is crucial when entering the Korean market because of its unique features, including:
Your market research should cover a very wide field, from import duties and other regulations to market-specific issues such as distribution channels, market size and growth, competition, demographics and local production. You may need to commission your own professional Korean-based research and visit the market numerous times.
Research organisations in Korea can be a major source of information. Austrade provides a range of services for Australian firms, including assistance on:
In addition to Austrade, the Queensland, Victorian, New South Wales and Western Australian state governments have representative offices in Korea and may be able to assist. The Australian Government's Export Market Development Grant (EMDG) scheme can help with costs, and state and territory governments may provide grants.
You will need to visit Korea to develop a deeper understanding of your target market and make contacts.
Visit before entering agreements with prospective agents, distributors or other business partners. Consider meeting with several potential partners to give you a basis for comparison. Arrange in-country assistance to help set up your program. This will help you see the right agents and customers who will be briefed and screened for interest and suitability. Numerous trade shows and exhibitions take place in Korea throughout the year, and can provide an excellent opportunity to meet potential customers.

Don't waste valuable time in Korea doing what you can do back in Australia. Training courses and seminars that can expand your knowledge about Korea and doing business there are offered by Asialink Business, Austrade, the Export Council of Australia and state and territory governments.
Pre-arrange as many of your meetings as possible and reconfirm meetings a day in advance. Carrying business cards is essential, and you should follow up with those who have given you theirs. Within 48 hours of each appointment, send an email thanking your contact for the meeting and providing follow-up information.
Sister-city and sister-state relationships can be useful, offering networking events and a network of existing relationships. Representative offices may also exist. Check with your local or state government.
Joining a business association is a great way to learn about the local business community and to meet potential colleagues and partners. In Seoul, there are several well-established country-specific business associations, including the Australian Chamber of Commerce in Korea (AustCham Korea), the Korean Chamber of Commerce and Industry (KCCI), and the Australia Korea Business Council (AKBC). Website details for each appear in Chapter 7.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
There are three primary ways to set up a business in Korea: set up a subsidiary, a branch office or a liaison (representative) office.
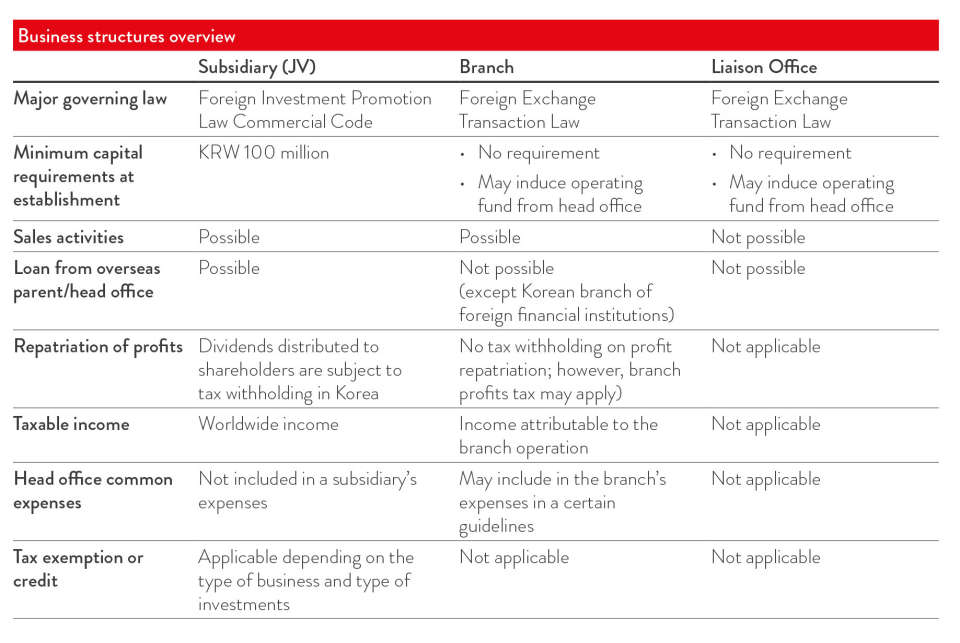
Setting up a subsidiary is a popular choice for foreigners. A subsidiary may be set up as either a joint stock company (Chusik Hoesa) or a limited liability company (Yuhan Hoesa). For the purposes of business operation there is no material difference between them, except that limited liability companies cannot issue bonds. Joint stock and limited liability companies are covered by the Foreign Investment Promotion Act (FIPA) and are the common structures for establishing a joint venture (JV) between a foreign investor and a Korean individual or entity.
All foreign companies – except those operating in sectors where foreign investment is restricted – may set up a branch in Korea. The establishment of a branch is completed upon registration at a relevant tax office and the court registry. Additional approval may be required from relevant ministries. Branch offices are subject to the Foreign Exchange Transactions Law, and may be established as either repatriating or non-repatriating entities.
Foreign companies are permitted to establish liaison (representative) offices in Korea. Compared to Joint Stock and limited liability companies, however, liaison offices have more restrictions and cannot conduct commercial business or generate revenue in Korea. Permitted activities include marketing or promotion, market research, review of business opportunities and research and development. Liaison offices are available for foreign companies engaged in all sectors of the Korean economy and are covered by the Foreign Exchange Transactions Act.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Korea is an attractive destination for high-end manufacturing thanks to its highly skilled workforce, world-class infrastructure, advanced research and development, and strategic location. But it is not a low-cost destination. The Korean Government encourages foreign investment in manufacturing and offers various incentives. Free trade, free economic and foreign investment zones offer specific incentives for high-tech manufacturers.
A joint venture with a Korean business is a popular option for foreign businesses wishing to establish manufacturing operations there; be it to produce a product for the Korean market or export. Another option is to engage a contract manufacturer to provide engineering and manufacturing services to companies that do not want to own and operate their own factories. They are typically experts in manufacturing and can quickly adopt your products into their manufacturing lines and schedules.
So how does Korea rank relative to other countries for ease of establishing business? The World Bank and International Finance Corporation in their Doing Business Report 2017, have compared 190 nations on nine specific measures related to establishing a business. As highlighted earlier, Korea was ranked fifth out of 190 economies for overall ease of doing business – with Singapore number two and Australia ranked 15th. They have particularly made starting a business easier by reducing costs, allowing online payment of registration taxes, setting time limits for value added tax registration and eliminating the minimum capital requirement and notarisation requirements.

For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?

You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Direct selling can be very effective in Korea. By utilising direct contact with buyers and end users, direct selling can be a cost-effective alternative to having your own base in the market, or using agents and distributors. But the do-it-yourself option is not easy. The main positives include:
On the negative side, having no physical presence in the market can make it difficult to progress. Many Koreans will not do business with companies that have no representation in the country. Also, recent trends include an increase in mobile internet/e-commerce retail sales, and a consumer shift towards mass retailers, which could prove challenging for direct sellers.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Franchising is a proven expansion technique for Australian brands looking to bring their goods and services to Korea. However, Korea has one of the more bureaucratic regimes in Asia for regulating franchises and the law does not distinguish between small domestic franchises and international franchise deals.
The most current research highlights that the Korean franchising sector is expansive and well developed. An average franchise in Korea operates 68 stores, with most in food service, followed by retail and then services. Australian businesses should note that Koreans are not willing to pay the large franchising fee often associated with franchising in Australia, and are generally attracted to well-established brands in Korea.
The Korean Government has made recent changes to the Fair Transaction in Franchise Business Act, designed to level the bargaining power between franchisees and franchisors. It is crucial that Australian franchisors seeking to operate in the Korean market keep up to date with changes.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Korea has a well-established and sophisticated e-commerce sector with online sales totalling AUD 75.1 billion in 2016. Mobile devices are increasingly used to make online purchases, with over 80 per cent of the Korean population using smartphones in 2015. Mobile retailing (also known as 'm-commerce') is quickly becoming the norm with purchases made on mobile devices now accounting for over 40 per cent of online sales, up from just over 15 per cent in 2013. Consumers are also familiar with crossborder e-commerce, as domestic products are often sold at a premium by retailers, thanks to agreements with manufacturers.
To sell online in Korea you are required to set up a subsidiary or open a branch office in the country. If you want to use popular online sales markets such as Gmarket, 11st, Shopping.Naver, Interpark, and Cjmall, Korean residential status is required. It is also recommended for Australian businesses potentially selling online in Korea to review privacy regulations, which may restrict management of user data on international servers.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Most Australian firms doing business in international markets rely on agents or distributors. It is critical that the responsibilities of representatives are clearly defined in any agreement you have with them.
Agent: Does not take ownership of goods being exported, but acts simply as a representative of the supplier. Agents are usually paid on commission. Based in the target market, they will often represent several complementary products or services. They can be retained exclusively as the sole agent for a company's goods or services or as one of a number of agents for the exporter in a particular market.
Distributor: Buys the goods from the exporter then resells them to local retailers or consumers. Distributors may carry complementary and competing lines and usually offer after-sales service. Their fees are higher than agents' because of associated costs; they usually carry inventory and are responsible for marketing.
Ensure you can establish a close working relationship with an agent or distributor – you must be able to build high levels of trust and regular communication. Meet with the potential partner in their own market, to get to know them better and observe how much they know. Ask for trade references and consider using a credit checking agency to confirm their financial stability.

For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Korean product lifecycles are much quicker than in Australia. A new product or brand's sales will explode but often decline just as precipitously. Individual consumers pick their goods, at least partly, in order to conform to group patterns. As a result, Korea has fewer niche markets than Australia, and it can be harder to forecast which products will be adopted next.
Korean consumers are strongly influenced by group dynamics and follow dominant trends. They tend to buy Korean-made cars, entertainment and spirits in order to confirm their status in society.
Various advertising mediums exist, including:
However, the power of the internet cannot be underestimated. Korea is the most wired country in the world, and an online presence is essential for marketing. Koreans in their 40s, 50s and even 60s make a high proportion of purchasing decisions based on what they find on their PCs and mobile phones.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
All food and beverage imports must be labelled in Korean. Labelling standards and import requirements can frequently change so be advised by Korean representatives for the latest information.
Shipments of plants, seeds, vegetable products, livestock, and animal products must be accompanied by sanitary certificates issued by the approved authority in the country of origin. In Australia, this is the Australian Quarantine and Inspection Service of the Department of Agriculture and Water Resources. Certificates are required for all pharmaceuticals, medical devices and health food products.
There is also the mandatory KC mark certification for certain manufactured products such as bedding and clothes for babies, chemical household items and automotive tyres. The list is extensive and is constantly updated.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?

Having chosen your strategy for establishing your business, you must consider how to conduct business in Korea.
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
The 2015 Australian International Business Survey (AIBS) identified local language, culture and business practicalities as the largest single barrier to Australian businesses conducting business in Korea. Korean culture is steeped in Confucianism, which emphasises respect for education, authority and age, and these principles underpin many customs and business practices.
Age and status: Respect for age and status are very important in Korean culture, with everyone having a role in society as a result of hierarchy. Koreans are most comfortable interacting with someone they consider their equal. Status is largely determined by someone's role in an organisation, which organisation they work for, which university they went to and their marital status.
Business cards: The exchange of business cards is an essential part of initial meetings. It allows Koreans to quickly determine their counterpart's all-important position, title and rank. While standing, you should hand a business card over with two hands, and receive one in return. Take some time to review names and titles.
Korean names: In Korea, the family name comes first (Kim Tae-Woo, for example). Until you are on very good terms with a Korean counterpart, it is best to use the family name preceded by an honorific (such as Mr). In settings that call for great respect or formality, you should use your counterpart's formal title and surname (Chairman Lee, for example).
Bowing and handshakes: Koreans bow to those senior to them both as a greeting and a show of respect. The junior person bends from the waist to an angle of 30 to 45 degrees from vertical. A less accentuated bow is returned from the senior person. For Australian business people, extending a simple handshake when greeting and taking leave is fine.
Building relationships Relationships are developed through informal social gatherings and generally involve a considerable amount of eating and drinking. Such gatherings also present the opportunity for both sides to discuss business in more relaxed surroundings.
Dress code: Koreans tend to dress more formally than Australians. Men should wear dark-coloured business suits with ties and white shirts. Women should also dress conservatively and in subdued colours.
Gender equality: Although gender equality is increasing, men still dominate the Korean workplace. It is expected that businesswomen act in a manner that is considered refined and “feminine".
Don't be too pushy: Korean business people are good negotiators so be patient and gentle, but firm. Be as dignified as possible and don't push too hard. Expect a “price war" but don't give in easily.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
The strength of business relationships can determine many aspects of commercial life, including access to credit, procurement and contracting. Investing in business relationships often involves large amounts of face-to-face time with a person of similar age and status, with a strong emphasis on loyalty and trustworthiness.
Formal introduction: Koreans prefer to do business with those they have a personal connection with. Being introduced through an intermediary is ideal. Cold calling typically has limited success.
Conscious effort: A conscious effort is required to nurture relationships and build trust. After your business has been set up, you should still send the most senior executive possible to Korea in order to avoid insult. If the most senior person is not available or does not have the expertise required, you might consider giving the individual with the most knowledge a high-status title. Keep Koreans informed of any personnel changes.
Socialise with Koreans: If potential business partners present an invitation to socialise, this is a positive sign and the offer should be taken up. A typical night out starts with dinner and may continue with drinking and karaoke.
Gifts: Gift giving is a part of business culture in Korea, and generally occurs at the start of a meeting after greetings. Gifts should be given and received with both hands and should not be opened in the presence of the giver. If you receive a gift, you should reciprocate with one of similar value. Gift wrapping is important in Korea so wrap carefully and avoid using dark colours.
Networking events: The typical style of networking in Korea comprises sit-down events, generally with dinner. Koreans find Western-style stand-up networking events uncomfortable and impersonal. If you're bringing your Korean business partners to such an event, make sure you brief them that it is a stand-up format.

Australians will need to consult some primary government agencies throughout the process of setting up a business in Korea.
KOTRA assists businesses in foreign trade through business match-making, trade missions, exhibitions, and by providing information on overseas markets. ( english.kotra.or.kr)
Invest KOREA, a branch of KOTRA, is the Korean Government's inward investment promotion agency. It provides assistance with administrative procedures for foreign investment into Korea, including consultation on mergers and acquisitions, joint ventures and real estate acquisition, and advice on legal and taxation matters. ( investkorea.org)
The Seoul Global Center – operated by the Seoul Metropolitan Government – functions much like Invest KOREA. It provides support for business start-up procedures in Seoul, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. ( global.seoul.go.kr)
Other useful departmental and association websites include:
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
It is considered polite to arrive on time or no more than a few minutes early for appointments. Arriving late is not recommended as it can be viewed as a snub by your host. If you are delayed, call ahead to inform your host.
At an initial meeting, be prepared to begin with small talk. Topics might include whether you are making a first visit to Korea, your impressions of the country, your family, favourite sports and other interests.
Koreans are very hospitable and friendly, but negotiations can be very aggressive in tone. You may find the Koreans can be very frank and quick to express anger and frustration. Nevertheless, you should not take everything said during these meetings literally; strive to maintain your composure and patience.
When negotiating over details, including price, your first bid should leave some room for negotiation. The starting positions of your Korean counterparts may appear unrealistic, but they will be prepared to compromise. In this way, both sides appear to have gained ground.
Be patient with delays in decision-making. Some Koreans may use stalling tactics to “wear down" the other side. However, things can move very fast if Koreans see the right business opportunity.
Koreans have a more flexible attitude towards contracts than Australians as they perceive them as a framework for a business relationship, and open to continuous adjustments over time. Even when aware of the legal implications of signing contracts, most Koreans view the contract as less important than the relationship between individuals and companies.

For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Companies involved in international commercial disputes should seek appropriate legal advice in Australia or overseas. Austrade can provide referrals to legal service providers upon request. A number of international arbitration commissions exist to facilitate international dispute resolution.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?

Australians conducting business in Korea need to deal with a host of local legal provisions, including laws and regulations covering tax, employment, importing, foreign investment, property, banking and repatriation of profits. Laws and regulations that may apply to your business in Korea are subject to frequent changes as the Government moves to attract more foreign investment and business operations to Korea. Further reforms are expected in January 2016.
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Foreign investment in Korea is governed by the Foreign Investment Promotion Act (FIPA). This act provides the legal basis for tax incentives and benefits relating to foreign direct investment, while underpinning the procedures for investment in Korea.
Foreign companies may invest in all but a small number of protected sectors, mainly involving communications and broadcasting. In some sectors, a joint venture (JV) with Korean companies may be required. To be considered a foreign investment company under FIPA, foreign companies must invest at least KRW 100 million and acquire 10 per cent or more of the voting shares or interest of a Korean company.
The Government organisation Invest Korea provides extensive services free of charge to foreign businesses, including consultation, assistance with investment notification and corporate establishment, support for business activities in Korea, and grievance resolution.
Government policies for investment promotion: The Korean Government has selected 17 industries expected to serve as future drivers of economic growth – and in which foreign investment is being promoted. They include: renewable energy, low-carbon energy technologies, green transportation systems, IT convergence citywide, LEDs in the green technology sector, broadcasting and communications media, intelligent robots, bio-pharmaceutical and medical devices, information technology, food industry and nano-convergence in the high-tech convergence sector, healthcare, green financing, cultural content and software, education, MICE (conventions and exhibitions), and tourism-related industries in the value added service sector.
Value added strategy in core industries: Korean companies are focusing on the development of high value-added products and services, such as hybrid and fuel cell-powered vehicles, and specialised ships that require core advanced technology and advanced materials. Opportunities exist for foreign companies to add knowledge and technology to these areas of industry.

“Green growth": “Low carbon, green growth" is expected to guide Korea's development over several decades, and the Government is encouraging foreign participation and expertise in high-tech industries and business services. Tax and other investment incentives are available and institutional hurdles and regulations are being removed. In 2012, Korea became the first country in Asia to pass laws mandating the launch of an emissions trading scheme (ETS). From 2015, participation in the ETS became mandatory for installations emitting 25,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide, and for firms emitting 125,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide annually.
In principle, foreigners are free to acquire land in Korea except for specified categories including military facilities, cultural assets, land set aside for ecological preservation, and some land on islands required for military purposes.
The Korean intellectual property (IP) system is advanced compared to many other countries in Asia. Korean companies are prolific filers of patent and trademark applications for inventions and local brands. In general terms, IP registration and protection in Korea is similar to Australia. The Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO) is responsible for the registration of trademarks, patents and designs – all of which can be applied for online. The KIPO website also provides a searchable patent database.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Tariffs and import regulations are frequently revised and subject to change without notice, so you should reconfirm your situation before exporting goods to Korea.
Korea has a two-column tariff scheme based on the international “harmonised system". Duties are mainly a percentage of the cost, insurance and freight (CIF) value, provided such value is based on current domestic value at date of export. Goods that meet the KAFTA preferential rates are subject to the reduction or elimination of tariffs on items originating from Australia.
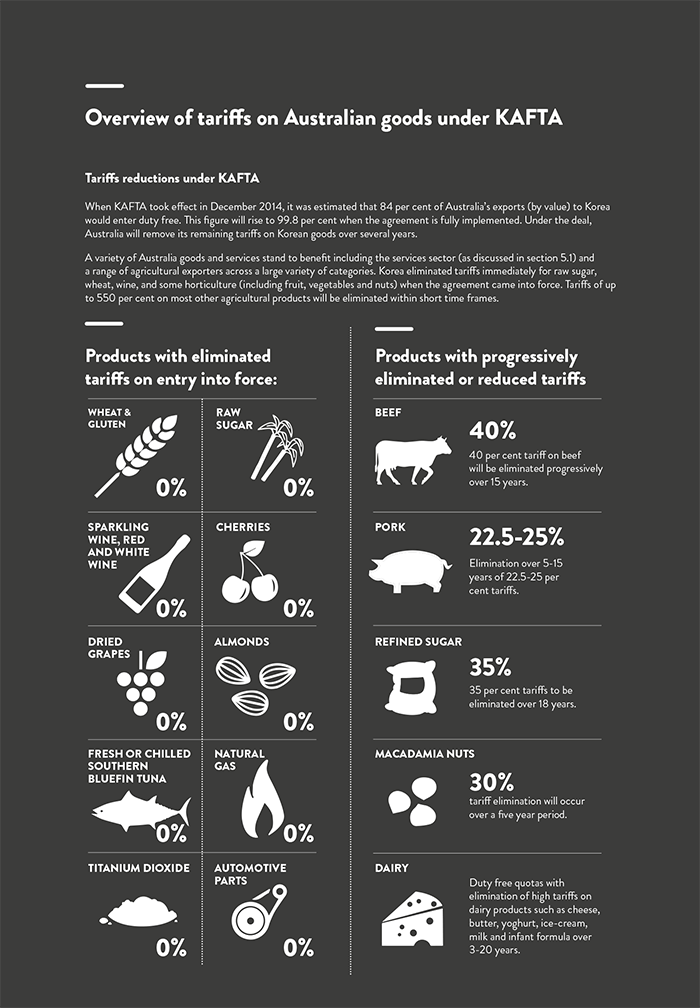
Other import duties: For items not covered under KAFTA, there are a variety of other import duties across various goods. These are often referred to in the Korean context as “custom duties".
Customs valuation: The dutiable value of imported goods includes the cost of the goods as well as insurance and freight (CIF). In 2008, the Korea Customs Service introduced the Advanced Customs Valuation Arrangement (ACVA), which provides a mechanism for taxpayers and the customs service to agree to an appropriate dutiable value of imported goods sourced from related parties.
Indirect tax: A flat 10 per cent value-added tax (VAT) is imposed on all imports unless customs duties on such imports are exempt. An individual excise tax of 5 to 20 per cent is also levied on the import of automobiles and certain luxury items.
Taxable value: The taxable value of imported goods is equal to the total amount of the transaction value for customs duties, individual excise tax and liquor tax (if any).
Indirect tax: A flat 10 per cent value-added tax (VAT) is imposed on all imports unless customs duties on such imports are exempt. An individual excise tax of 5 to 20 per cent is also levied on the import of automobiles and certain luxury items.
To further explore the benefits of KAFTA for Australian businesses, refer to the FTA Tool developed by the Export Council of Australia. This website helps Australian exporters navigate the basics of Australia's Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) quickly and easily.
www.ftatool.com.au
The Korean Government requires that all importers have a general licence or a special licence for all imported items. The Ministry of Strategy and Finance is required to pre-approve imports that are to be exempt from customs duties. Restrictive regulations govern the content and safety of products. Some consumer goods such as food, pharmaceuticals and toys are subject to more stringent examination.

For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
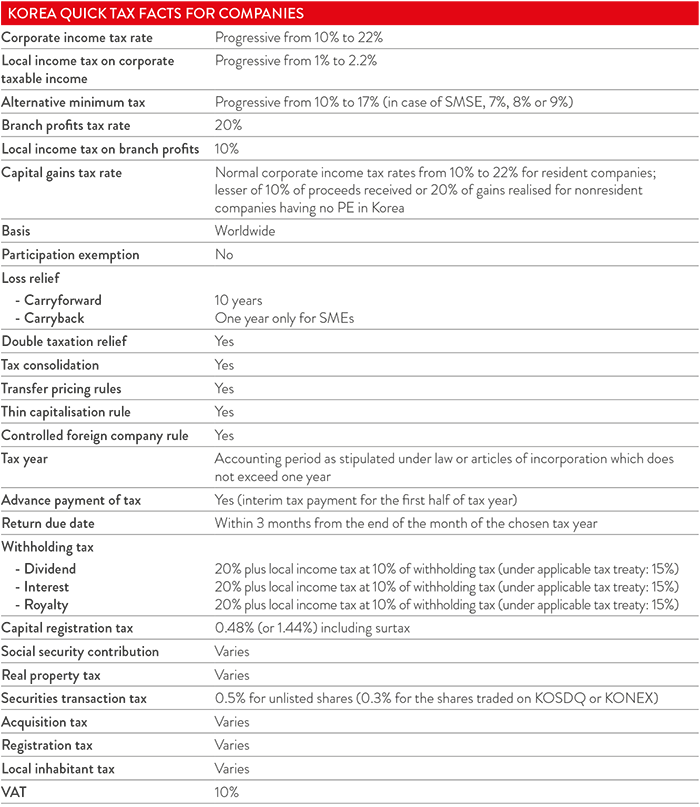
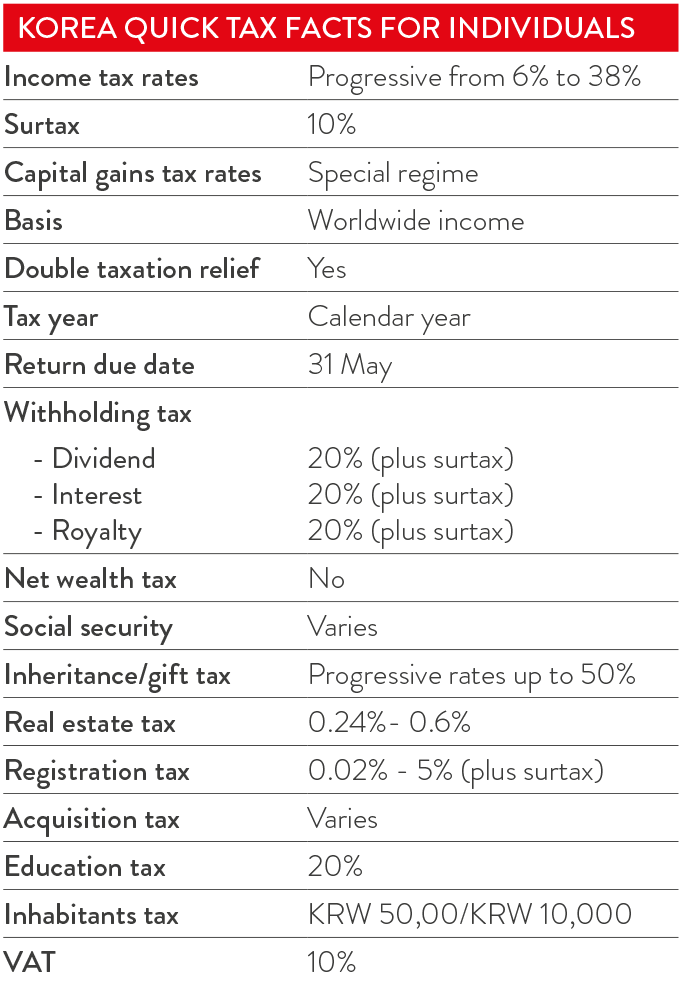
Korea's taxation system includes a wide range of imposts on businesses and individuals, including income taxes (corporate income tax, local income tax and individual income tax), turnover taxes (value added tax and excise tax), as well as taxes such as surtax and acquisition tax. This is not a comprehensive guide to tax in Korea, and all businesses should seek professional tax advice when setting up.
Corporate income tax (CIT) in Korea is covered under the Corporate Income Tax Law (CITL), the FIPA, the Special Tax Treatment Control Law (STTCL) and the Law for the Co-ordination of International Tax Affairs (LCITA). Taxes are administered and collected by the National Tax Service (NTS). Although CITL distinguishes between foreign and domestic companies, most provisions apply to both. Foreign entities, however, are eligible for tax incentives thanks to FIPA and the STTCL, and may also be eligible for further tax savings if they set up in foreign investment and free trade zones.
Corporate taxpayers fall into two classifications:
Resident corporation: A domestic corporation with its head office, main office or place of effective management in Korea, taxed on its worldwide income.
Non-resident corporation: Foreign corporation that earns income from domestic sources in Korea, taxed only on income derived from Korea.
Taxation of foreign corporations/shareholders: If a foreign corporation has no “domestic place of business" in Korea, it will be subject to tax on its Korean-source income on a withholding basis in accordance with the tax laws and any applicable tax treaty. Any Korean source income to a domestic fixed place of business of a foreign corporation will be subject to Korean income tax.
Permanent establishment (PE): A non-resident corporation is generally deemed to have a tax presence, i.e. a domestic place of business in Korea, if one of the following applies:
Dependent agent PE: Generally, an agent of a foreign corporation who frequently exercises authority to conclude contracts in the name of the foreign corporation, or who maintains a stock of goods or merchandise in Korea belonging to a foreign corporation from which the agent regularly orders on behalf of the foreign corporation, will be deemed to be a PE of the foreign corporation in Korea.
Branch income: In general, a branch office of a foreign corporation is taxed in the same manner as a resident company. Remittance of retained earnings from a Korean branch to its head office is subject to reporting to a designated foreign exchange bank in Korea.
Tax rates: The basic CIT rates are 10 per cent on the first KRW 200 million, 20 per cent for any amounts between KRW 200 million and 20 billion, and 22 per cent for the excess. Resident corporations are taxed on their worldwide income, whereas non-resident corporations with a permanent establishment in Korea are taxed only to the extent of their Korean-sourced income. Non-resident corporations without a PE in Korea are generally taxed through a withholding tax (WHT) on each separate item of income. For SMEs, the minimum CIT is the greater of 7 per cent of adjusted taxable income or actual tax liability.
Taxable income: Income from all sources (including business income, dividends, rents, interest, royalties, salaries and profit realised from the sale of property), whether received inside or outside Korea, is subject to CIT. Exceptions apply in some instances, including income earned outside Korea by non-resident aliens.
Deductions: In general, expenses incurred in the ordinary course of business are deductible. A corporation's disbursements of more than KRW 30,000 for goods or services provided must be supported by corroborating documents, which must be maintained for five years. Accrued expenses are not deductible until the expenses are fixed or paid.
Foreign corporations having a PE in Korea with income derived from sources in Korea are subject to CIT on such income. If the foreign corporation has no “domestic place of business" in Korea, it will be subject to tax on its Korean-source income on a withholding basis. Any Korean-source income attributable to a domestic fixed place of business of a foreign corporation will be subject to CIT. For residents of countries having a tax treaty with Korea such as Australia, the reduced WHT rate is 15 per cent (for dividends, interest and royalties).
There are four types of social security contributions in Korea: national pension, national health insurance, employment insurance and workers' accident compensation insurance. Employers and employees are required on an almost equal basis to contribute 8.185 per cent of salaries for pension, health and employment insurance. The worker's accident compensation insurance and employment insurance at 0.25-0.85 per cent (depending on number of employees) is additionally borne by employers only.
VAT is levied at 10 per cent on the supply of goods and services. Some goods and services are exempt (basic life necessities and services such as unprocessed foodstuffs, medical and health services, finance and insurance services, and duty-exempt goods). Electronic VAT invoicing is compulsory.
The basic local income tax rates for a corporation are 1 per cent on the first KRW 200 million, 2 per cent between KRW 200 million and KRW 20 billion, and 2.2 per cent for the excess.
These include property taxes, stamp tax and an individual consumption tax on items including luxury goods.
This is imposed on certain luxury goods, high-priced durable consumer goods, goods subject to consumption restraints, and certain luxury activities. Tax rates range from 2 per cent to 20 per cent.
An annual tax ranging from 0.07 to 5 per cent is charged on the statutory value of land, buildings, houses, vessels and aircraft. A factory that is newly constructed or expanded in certain metropolitan areas attracts five times the property tax rate for five years from its relevant registration date.
Charged on the purchase price of real estate, motor vehicles, construction equipment, golf membership, boats and other items. The minimum rate is 1 per cent.
Stamp tax (known in Australia as stamp duty) is levied on a person who prepares a document certifying establishment, transfer, or change of rights to property in Korea. The stamp tax ranges from KRW 100 to KRW 350,000, depending on the type of taxable document.
Registration tax ranging from 0.1 to 5 per cent is charged upon the act of registering the creation, alteration or lapse of property rights or other titles and incorporation with the relevant authorities.
Gift tax is imposed on a person who acquires property by gift. If CIT or individual income tax is imposed on the gifted property, however, the gift tax shall not be imposed. Gift tax ranges from 10 per cent on gifts valued at not more than KRW 100 million, to the top marginal tax rate of 50 per cent.
In Korea, taxpayers can choose their own fiscal-year dates and cycles if the relevant law or articles of incorporation does not stipulate the accounting period. A corporation must file an interim tax return with due payment for the first six months of the fiscal year, and the filing/payment must be made within two months after the end of the interim six-month period.
A corporation must file an annual tax return with due payment for the fiscal year, and the filing/payment must be made within three months from the end of the month that the fiscal year end date belongs to. In many circumstances, tax may be paid in instalments.
Korea and Australia have a tax treaty that aims to eliminate double taxation. Tax paid in Australia on foreign income may be credited against Korean income tax. The amount credited is limited to the lower amount of foreign taxes paid and additional Korean tax due to the inclusion of the foreign income.
Under the Special Tax Treatment Control Law (STTCL), some tax reductions or exemptions are available for foreign-invested corporations as well as certain SMEs. Tax credits are also available to promote research and development. Temporary tax holidays are introduced from time to time based on government policy. There are also tax incentives relevant to international capital transactions, to facilitate restructuring of corporations and financial institutions, to promote job creation and to encourage the relocation of head offices or factories in urban cities to rural areas.
Various tax incentives are granted to SMEs. These include a special tax exemption that ranges from 5 to 30 per cent of taxable income. Also, with the acquisition of some business assets, 3 per cent of the acquisition cost is deducted from corporate income tax. In addition, newly incorporated SMEs in non-metropolitan areas are given a 50 per cent reduction in corporate income tax for five years.
Taxes imposed by foreign governments on income declared by a resident taxpayer are allowed as a credit (within specified limits) against income taxes to be paid in Korea, or as deductible expenses.
If the number of regular employees in a current year does not decrease compared with that in the previous year, investments that create jobs attract a tax credit of 3 to 9 per cent. The credit for an investment that maintains the same employment numbers is 1 to 3 per cent and is only available for certain companies like SMEs.
Various tax incentives are provided to stimulate R&D activities including deduction of R&D reserve, tax credits for research, and manpower development expenses.
Tax credits are generally available for investments in facilities that enhance productivity, safety, job creation, and other aspects of a business.
Foreign invested companies that engage in certain high-technology businesses, and service businesses that provide extensive support to such industries, can apply for exemptions from corporate income tax and local taxes such as acquisition tax and property tax. Approved foreign investment also can be eligible for exemption from customs duties, VAT, and special excise tax on imported capital goods.
Foreign investors satisfying specified criteria are provided with tax incentives and other benefits for investment in specially designated areas, including foreign investment zones (FIZ), free economic zones (FEZ), free trade zones (FTZ), and strategic industrial complexes exclusively developed for foreign invested companies. The tax incentives for qualifying foreign investors in FIZ are similar to those of foreign invested high-tech companies.
Individuals with a domicile in Korea for 183 days or more are considered residents for tax purposes. Even when a person has a job overseas and stayed overseas for more than 183 days, but they have their general living relationship including their family and property in Korea, they can be regarded as a resident of Korea.
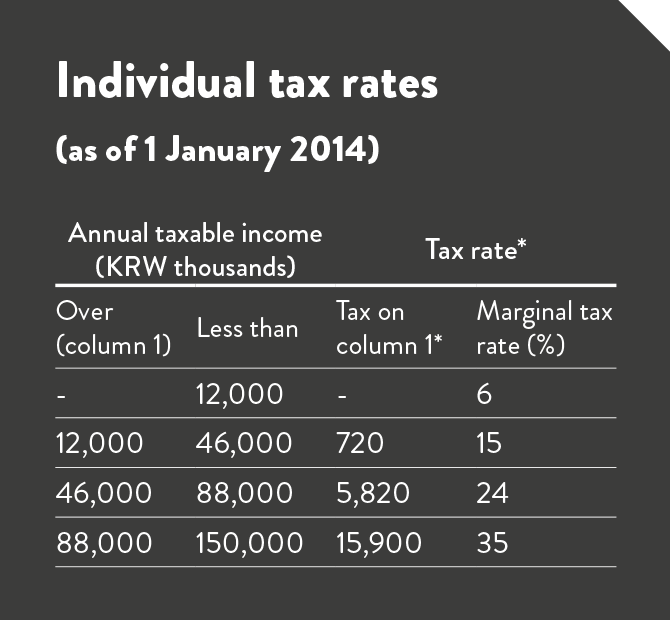
Currently, the individual tax rates on global income range from 6 to 38 per cent before applying the local income tax (ranging from 0.6 per cent to 3.8 per cent of individual taxable income). The top marginal tax rate of 38 per cent is applied to taxable income in excess of KRW 150 million.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Korean commercial law requires that accounting records explain a company's transactions and any effects these have on its operational assets. Accounting records are normally required to be retained for 10 years.
Most businesses have the period 1 January to 31 December as their accounting period.
Business entities generally follow the accrual basis of accounting. All income realised and expenses incurred or attributable to the current period should be recognised as income or expenses in the current period regardless of when the income is received or expenses are paid.
A stock company that meets certain criteria is required to have its financial statements audited by an external auditor.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Korea's labour force is generally regarded as highly literate, well-educated, motivated and hard working. Its abundant supply of skilled labour has played a primary role in making it a world leader in industries such as shipbuilding, vehicle manufacturing and steel making.
Koreans are diligent and faithful to their work. In 2014, Koreans' average annual working hours were 2124 – the second highest among OECD countries.
As a nation, Korea is passionate about education. Enrolment rates at all levels of education are among the highest in the world. These factors, combined with the country's high degree of technological adoption and relatively strong business sophistication, help explain its remarkable capacity for innovation.
The Labour Law of Korea sets standards for labour contracts and relations between employers and workers and enables autonomous dispute resolution between labour and management by guaranteeing workers' right to organise a union, and aims to promote the participation and co-operation of both employers and workers.
Minimum conditions for employees are set out in the Labour Standards Act, and the Employment Insurance Act grants benefits to jobless workers and aims to improve employee skills and employability. Compensation and insurance coverage for industrial accidents is guaranteed in the Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance Act.
Under Korea's Minimum Wage Law, mandatory minimum wage standards applicable to all firms in all industries are set and reviewed annually by the Minister of Labour.
Social insurance programs covering pension funds, medical costs, workplace accident compensation and employment insurance must be contributed to by employers. Employers and employees each contribute 4.5 per cent of the employee's monthly salary to the national pension fund. Employment insurance provides 50 per cent of previous wages for up to eight months for unemployed workers up to the age of 64, provided they had been employed for six months or more.
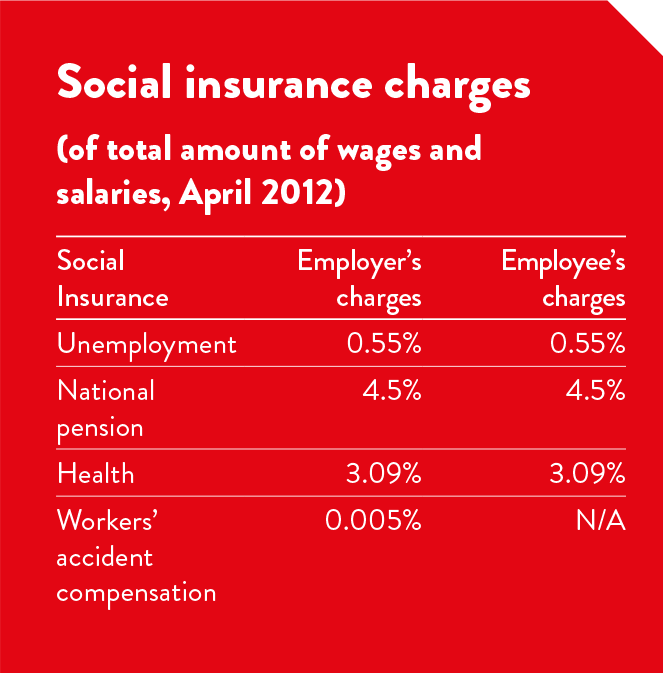
On annual leave, the Korean Standards Labour Act states that an employer should grant 15 days paid leave to a worker who has registered more than 80 per cent of attendance in a year. After the first year of service, an employer should grant one day paid leave for each two years of consecutive service in addition to the leave for the first year.
Australians who are working or have worked in Korea are able to receive a lump-sum refund of their social security contributions or have access to a Korean old-age pension.
It is possible to dismiss an employee for a legitimate reason and with 30 days advance written notice or payment of a month's wage. However, a Labour Dispute Mediation Committee exists for conciliation, mediation and arbitration of labour grievances. If a worker continuously employed for one year or more is terminated for any reason, severance pay of at least one month, or pay equivalent to an average of 30 days, must be paid for every year of employment.
Labour market inflexibility and hostile labour-management relations have in the past been considered prime factors hindering the attraction of foreign investment in Korea and efficient utilisation of labour. The Korean Government has in recent years strived to achieve stabilisation in labour-management relations, and this has been reflected in a more stable environment with a continuing decline in the number of illegal and other labour disputes.
There are almost 4500 company-based unions in Korea as well as several industry unions. Union and union-eligible Korean employees are estimated to number around 15 million out of a total workforce of 23.5 million. Starting around June every year, trade unions gear up for industry-level collective bargaining.
Successful recruiting requires developing a strong company brand and word of mouth to compete with the better-known local players. The company's vision for the future must be credible, and marketing messages have to be tailored to meet the unique characteristics of the Korean business environment. Offering a better work-life balance can switch the recruiting advantage to the foreign company.
A foreigner who wishes to reside in Korea must have a visa which allows an appropriate period of stay (theoretically not less than 91 days but normally six months or longer). If a visa is granted for 90 days or less, it cannot normally be extended while the foreigner is in Korea. The extension requirements are waived for a foreigner who has invested at least USD 500,000 under the FIPL with the employment of five or more workers.
Foreigners seeking employment in Korea must have a work visa. The first alternative is a Technology Inducement Contract (TIC). Under this arrangement, employees of the foreign licensor would enter Korea for work under the TIC. Second, expatriates may be sent to Korea for work at a foreign entity's branch office. Third, expatriates may be hired by a Korean company (foreign invested company or join ventures under the FIPL). Certain types of visa status are most suitable for expatriates. A foreigner holding any of these types of visa status may stay in Korea for up to four years.
Australian businesses should adapt their management styles to accommodate local preferences. Social hierarchy and loss of face are key issues. Managers should also encourage social interaction in the workplace.
Lower-level employees in Korea will generally be reluctant to question authority or even to provide feedback. Australians managing Korean employees will be expected to take a much closer interest in the personal lives and welfare of workers than would be expected back home. And don't be surprised when your staff arrive before you and leave after you – they will do that no matter what time you come and go as a way of showing their dedication.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
The banking system in Korea is advanced and relatively user-friendly. Most of the well-known banks have service representatives who speak some English, and many offer internet banking in English or accounts tailored to expat needs. ATMs of major banks in Korea generally have an English option.

Financial institutions in Korea are classified into the following broad groups: banks, non-bank financial institutions, financial investment services companies, and financial holding companies. Korea's commercial banking system remains sound, liquid and well capitalised in the wake of the global financial crisis.
Australian banks in Korea: At present only ANZ operates a full subsidiary in Seoul.
Foreign bank accounts, including Australian accounts, can be accessed from ATMs around Korea. If you have a Korean bank account, this cannot be accessed from outside Korea unless requested.

Currency exchange: When exchanging less than KRW 1 million in a single transaction, you will need your passport or alien registration card for identification. For amounts greater than KRW 1 million, the bank teller will record the transaction in your passport.
Overseas remittance Foreigners can send up to USD 50,000 out of the country per year. This can be done in a branch, online or through an ATM. To send more than USD 50,000, evidence in the form of tax returns and other official documents showing where the money came from must be presented. Once the USD 50,000 limit has been reached, remittances must be made at a bank branch. Individuals cannot take out more than USD 10,000 from Korea.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Most transactions involving foreign exchange generally do not require approval or reporting. Receipt of foreign exchange from outside Korea is freely permitted, and payments to foreign companies are not regulated. Most foreign currency loans are allowed and are subject to reporting to a foreign exchange bank.
Korea's foreign exchange controls are in line with OECD standards. Reporting requirements and some controls remain in place on forex payments made by individuals and businesses. Korean law protects the repatriation of approved capital and remittance of dividends and profits.
Foreign businesses that invest under the terms of the Foreign Investment Promotion Act (FIPA) are permitted to remit a significant portion of their profits. Businesses that do not invest and register under the FIPA may not remit retained earnings via a forex bank.
Korea's financial system is at times hard-pressed to fulfil requests for capital and financing for cross-border commercial transactions. This is because banks are required to maintain high capital adequacy ratios for their lending to SMEs. As a result, foreign companies in JVs with Korean partners usually provide the financing, while the Korean party makes in-kind investments such as land and facilities.
If a foreign investor complies with all reporting and approval requirements, the Foreign Investment Promotion Law guarantees the investor's right to repatriate income earned from the ownership of shares or equity interest, proceeds on disposal of such assets, principal and interest earned on long-term loan agreements, and payments received pursuant to technology licensing agreements. Repatriation methods include the sale of shares, receipt of dividends and other distributions, or a capital reduction.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Australians visiting Korea for transit, tourism, conference or business meetings do not need a visa for stays of up to 90 days, but must have a passport that is valid for at least six months and an outbound travel ticket. Australian business people undertaking activities relating to remuneration will require a visa. There are several visas available based on what industry you're in and the purpose of your visit. Contact the Korean Embassy or nearest Consulate for more information as visa requirements and fees regularly change.
A single-entry business visa is valid for stays of up to three months and can be obtained from the Korean Embassy in Canberra or the Korean consular offices in Sydney and Melbourne. If you are a frequent business traveller to Korea, it may be worth considering a multiple-entry business visa, which is valid for one year.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
The official currency of Korea is the Won, which is abbreviated to KRW or ₩. ATMs are plentiful in cities and most will have an English option after you insert the card. Look for ATMs displaying an “international cards accepted" notification, as often only one of a group of ATMs will accept foreign cards. International credit cards may only be readily accepted in larger hotels and stores.
Foreign currency can be exchanged at banks, airports and some hotels and tourist areas. You may find it more difficult to exchange KRW for other currencies outside of Korea.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Incheon International Airport, 52 kilometres from the centre of Seoul, is the main gateway to Korea. Taxis, trains and limousine buses connect the airport and downtown Seoul. Some regional international flights also operate from Gimpo Airport (Seoul) and Busan (Korea's largest trading port). Airport buses link the Incheon and Gimpo airports (approximately 30 minutes travelling time). Airport limousine buses, taxis and the subway also service Gimpo Airport from Seoul.
Domestic travel in Korea is relatively easy, with frequent train and air services connecting Seoul to major cities such as Busan and Daegu. Domestic flights out of Seoul mostly operate from Gimpo International Airport.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Taxis can be found at designated taxi ranks in most busy city areas or hailed on the streets. Some taxis can also be ordered by phone. While most taxis in the Seoul area accept credit cards or even pre-paid public transportation cards, you may need to pay in cash in small provincial cities and regional areas. Writing the destination down can help as most Koreans are better at understanding written rather than spoken English. All taxis have meters and many accept credit cards.
International taxis have drivers who can speak English or Japanese. These taxis operate on a reservation basis, and fares can be calculated by meter, by destination, or by time. International taxis tend to be orange and always have “International Taxi" written on a sign on the roof and the door.
If you're considering driving in Korea you'll need an International Driving Permit. Make sure you also have comprehensive insurance. Criminal charges and heavy penalties are common when accidents result in injury, even if guilt is not proved.
Express and Intercity buses are the most popular way to get from region to region with an extensive network offering a comfortable and convenient way to get around. However, the schedules vary and travel time can be lengthy compared to trains.
One of the most convenient ways to travel between cities in Korea is by train. Korean trains are classified based on their speed and the amenities offered onboard. The high-speed KTX travels between Seoul, Busan, Daejeon and Mokpo, with slower intercity Saemaeul trains providing services to other cities. The KR Pass, an exclusive railway pass for foreigners, allows unlimited use of all trains including KTX express trains for a certain number of days.
Seoul and other major cities also have subways, which are often the fastest option in peak traffic periods. Most subway signs are in both Korean and English. Subway tickets can be bought at all stations from ticket vending and card reloading machines, which have instructions in English, Korean and Japanese. You can choose between single-journey cards and multiple-journey cards, or buy a “T-money Card", which is rechargeable and can be used on subways, taxis and buses. There is also the “M-Pass" (Metropolitan Pass) offering limited rides (up to 20 per day) on subways in the Seoul metropolitan city area.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Seoul encompasses a collection of ancient palaces, sacred mountains, and a mixture of shopping districts, bright lights and trendy cafes and bars. It has more than 10 million residents and 25 major districts.
There is a large array of accommodation options (see the KTO website) to choose from, including many full-service international hotels, and serviced residences. Most international hotels are located in one of three main business areas: Jong-no, Gangnam and Yeouido. It is best to choose a hotel close to your meeting locations. North of the Han River is ideal if you want to stay within a lively area.
When trying to find your way to a meeting in Korea, be aware that buildings have historically been numbered based on the date they were built in each district, not by location. This means buildings next to each other can have completely different address numbers. The best way to get around is to have the address written or printed out in Korean to show to taxi drivers, who can then put the address into their GPS systems.

Business entertaining can be a critical relationship-building element of your visits to Korea. A great deal of relationship building takes place in bars and restaurants. Always accept dinner invitations as this is the Korean's opportunity to assess your trustworthiness and whether they wish to conduct business with you.
Dinner is the largest meal of the day and normally occurs between 7pm and 9pm. It is customary for the host to order the food, which all arrives at the same time. Korean food can be extremely spicy but milder dishes are also available. The host is expected to pay for the meal; nevertheless, a good-natured argument over who will pay is to be expected. It is also polite for the foreigner to offer a reciprocal dinner invitation.
Some other aspects of dinner etiquette to note:
Korea has one of the highest per capita alcohol consumption rates in the world so don't be surprised by the amount of alcohol that can be offered or consumed at business dinners. You do not have to take part in drinking if you do not want to but Koreans will prefer you to join in. The Korean tradition is that you never fill your own glass. As soon as you empty your glass it symbolises to your host that you want a refill. If you are a light drinker, keep your glass half full.
Tipping is not customary in Korea, although many restaurants will add a service charge to the bill.
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Most of the following information on health and welfare in Korea has been provided by the Australian Government's Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT) as general advice.
Australians should take out comprehensive travel insurance that will cover any overseas medical costs.
Water-borne, food-borne and other infectious diseases (including tuberculosis, typhoid and hepatitis) occur sporadically. It is advisable to avoid raw and undercooked food. In rural areas, it is recommended that all drinking water be boiled or that you drink bottled water.
Consult a travel doctor before travelling and ensure that your vaccinations against diseases such as hepatitis and tetanus are up to date.
Malaria is a risk in the Korean demilitarised zone and in rural areas in the northern parts of Gyeonggi and Gangwon provinces, near the border with North Korea. The mosquito-borne disease Japanese encephalitis also occurs. You should consult your doctor or travel clinic about prophylaxes against malaria and take measures to avoid mosquito bites.
As in many parts of industrialised Asia, Korea faces increasing health problems due to pollution in cities. In spring, the “Yellow Dust" – a combination of industrial pollutants and dust from mainland China – prompts some people to wear masks while outdoors.

Healthcare in Korea is modern and efficient.
Healthcare in Korea is modern and efficient. Both Western and Eastern medical practitioners and medicines are available, and both are covered under the Government's National Health Insurance (NHI) which foreign residents may be eligible for.
Foreigners can phone the Emergency Medical Information Centre for emergency or routine medical advice, or to help translate if they are at a clinic or doctor's office where nobody speaks English.
City hospitals will almost always have an English-speaking doctor on staff. Hospitals are often well equipped and modern, although may not always have the best sanitation practices. Foreigners can also attend “international clinics" affiliated with certain hospitals. These are staffed by doctors who have studied abroad and generally speak English well, but they are more costly. Patients generally need to pay a deposit against the costs that might be incurred during their stay.
Korea's National Health Insurance (NHI) program is a compulsory system that covers the whole population for most day-to-day and emergency medical procedures, prescription medication and specialist visits. By law, any company that employs more than five foreign workers must enrol their foreign workers in a health insurance program. The company is expected to pay 50 per cent of their employees' health insurance premiums each month, and employees the other half. To enrol in the NHI, expats simply need to bring their Alien Registration Card to a nearby hospital and apply. Once enrolled in the NHI program, you can extend your coverage to immediate family members.
Apart from the NHI, there are a number of private health insurance options; however, most of these are more expensive and not as widely recognised as the national scheme. Australians should note that some procedures and medications, particularly those associated with chronic illnesses such as cancer, are not covered under the NHI and can become costly.
Crime rates in Korea are low by international standards, making it a relatively safe country to visit.
Relations between Korea and North Korea remain tense, occasionally resulting in exchanges of live fire between border forces. The Australian Government continues to advise against all travel to the Northern Limit Line islands, near a disputed sea border. It also recommends that Australian citizens avoid protests and demonstrations, as they can turn violent.
Korean authorities conduct nationwide civil emergency exercises on the 15th day of each month except January, February, July and December. This involves the sounding of sirens, stopping of transport and some people are asked to take shelter in metro stations or basements.
June to July is monsoon season in Korea. Although the typhoons are not as bad as in some other Asian countries, schools and businesses sometimes close due to the severity of approaching storms.
Korean laws and penalties can appear harsh by Australian standards, and apply equally to foreigners and locals. You should be aware that:
Appearance is important in Korea, so it is important that you look your smartest at all times. The conservative convention of dark suit, shirt and tie is still the norm in Korea for men, while smart business suits or dresses are preferred for women.
Conservatism in dress is still valued by most Koreans. Ensure the following:
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
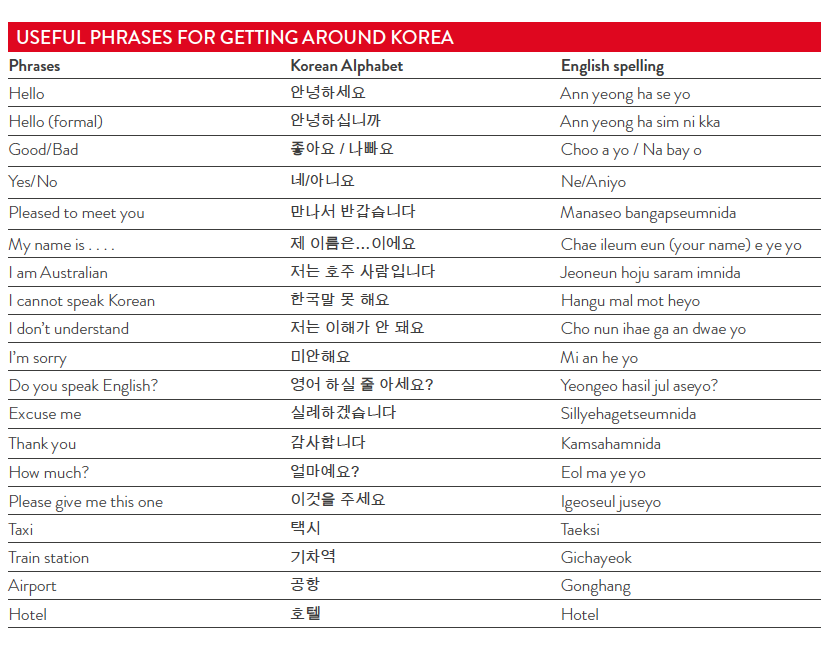
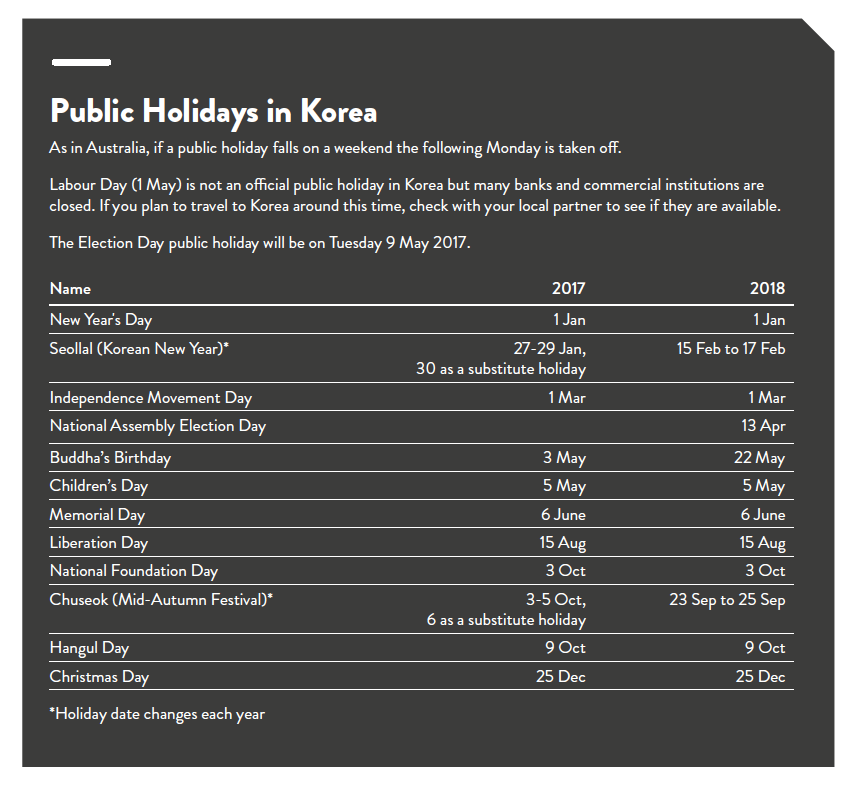
For more information, access the full Korea Country Starter Pack
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?

Asialink Business provides high-calibre opportunities for Australian businesses to build the Asia capability of their executives and team members. Our business-focused cultural competency programs, professional development opportunities and practical research products allow businesses to develop essential knowledge of contemporary Asian markets, business environments, cultures and political landscapes.
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
This app requires Google Chrome to continue. Tap the icon, copy link, then paste into Chrome
This app requires Google Chrome to continue. Tap the icon, Open in browser, then choose Chrome
Korea CSP
| App category: | Other |
| Updated: | May 17, 2017 |
| App Publisher: | Asialink Business |
| Compatible with: | iOS 6+, Android 4+, Blackberry 10+ and Windows Phone 8+. |
| Legals: | Terms of use |
You successfully shared the app
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://koreacsp.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?